Ringworm
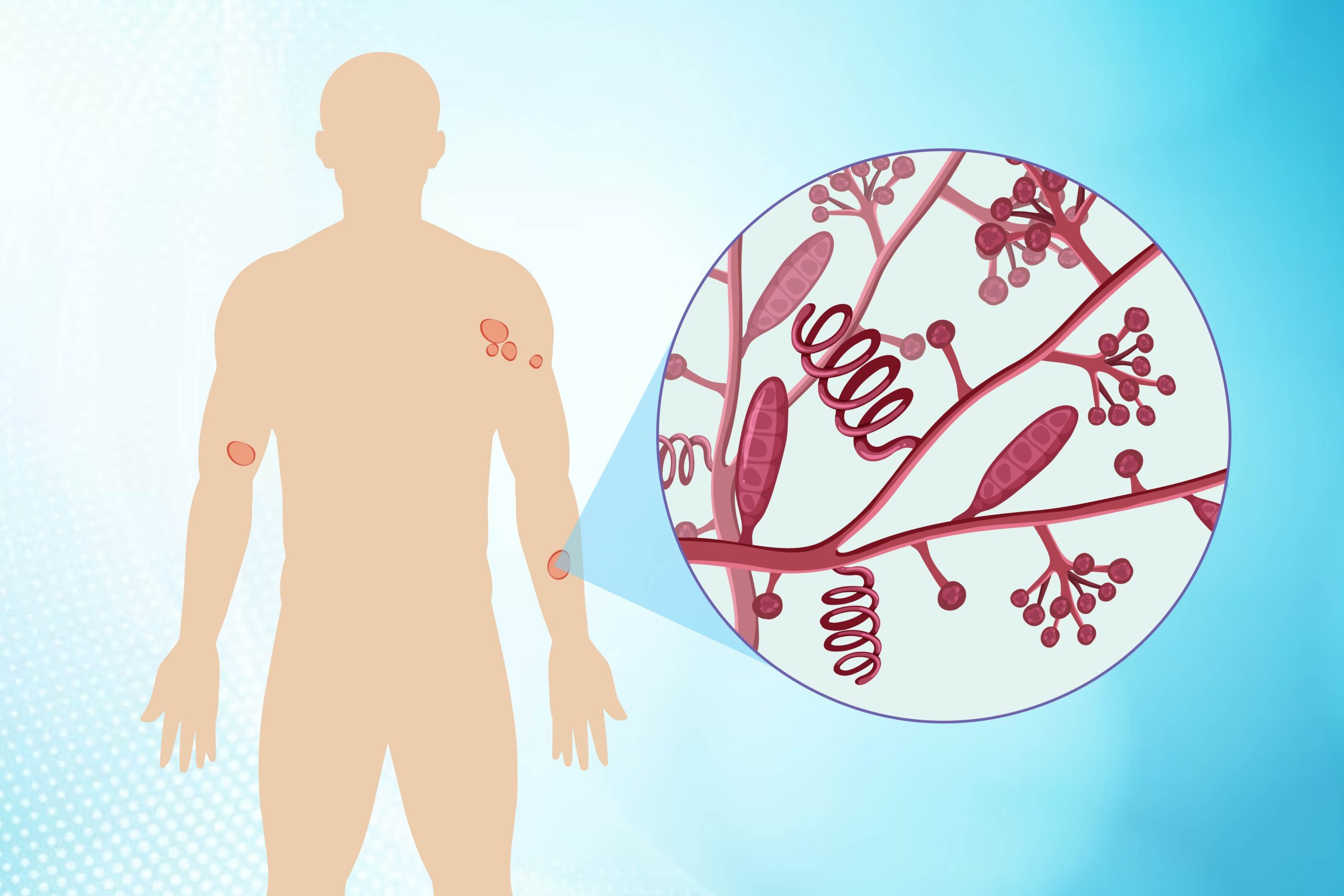
Overview
Ringworm, also known as tinea, is a common fungal infection of the skin. Despite its name, it is not caused by a worm but rather by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. Ringworm can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, feet, nails, and groin area.
Ringworm is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or object. Treatment for ringworm typically involves antifungal medications, which may be applied topically or taken orally. In addition to medication, it is important to practice good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items such as towels or combs to prevent the spread of the infection.
Symptoms
Red, itchy, or scaly patches on the skin
Circular or oval-shaped patches with raised, defined borders
Skin that appears swollen, blistered, or cracked
Hair loss or bald patches
Brittle, thickened, or discolored nails
Treatments
The treatment for ringworm usually involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally. The specific treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection.
For mild cases of ringworm, an over-the-counter antifungal cream or ointment can be applied directly to the affected area. These medications usually contain ingredients such as clotrimazole, terbinafine, or miconazole. It is important to apply the medication as directed, and to continue treatment for the full length of time recommended, even if the symptoms appear to have cleared up.
For more severe or widespread cases of ringworm, or for infections that affect the scalp or nails, prescription antifungal medications may be necessary. These medications may be applied topically or taken orally, and may include medications such as fluconazole, griseofulvin, or itraconazole. In some cases, a combination of topical and oral medication may be recommended.
In addition to medication, it is important to practice good hygiene and to avoid sharing personal items such as towels or combs to prevent the spread of the infection. It is also important to keep the affected area clean and dry, and to avoid scratching the rash to prevent further irritation and the spread of the infection.
Ringworm is a common fungal infection of the skin.
- Red, itchy, or scaly patches on the skin
- Circular or oval-shaped patches with raised, defined borders
- Skin that appears swollen, blistered, or cracked
- Hair loss or bald patches





