Mini Stroke (TIA)
Overview
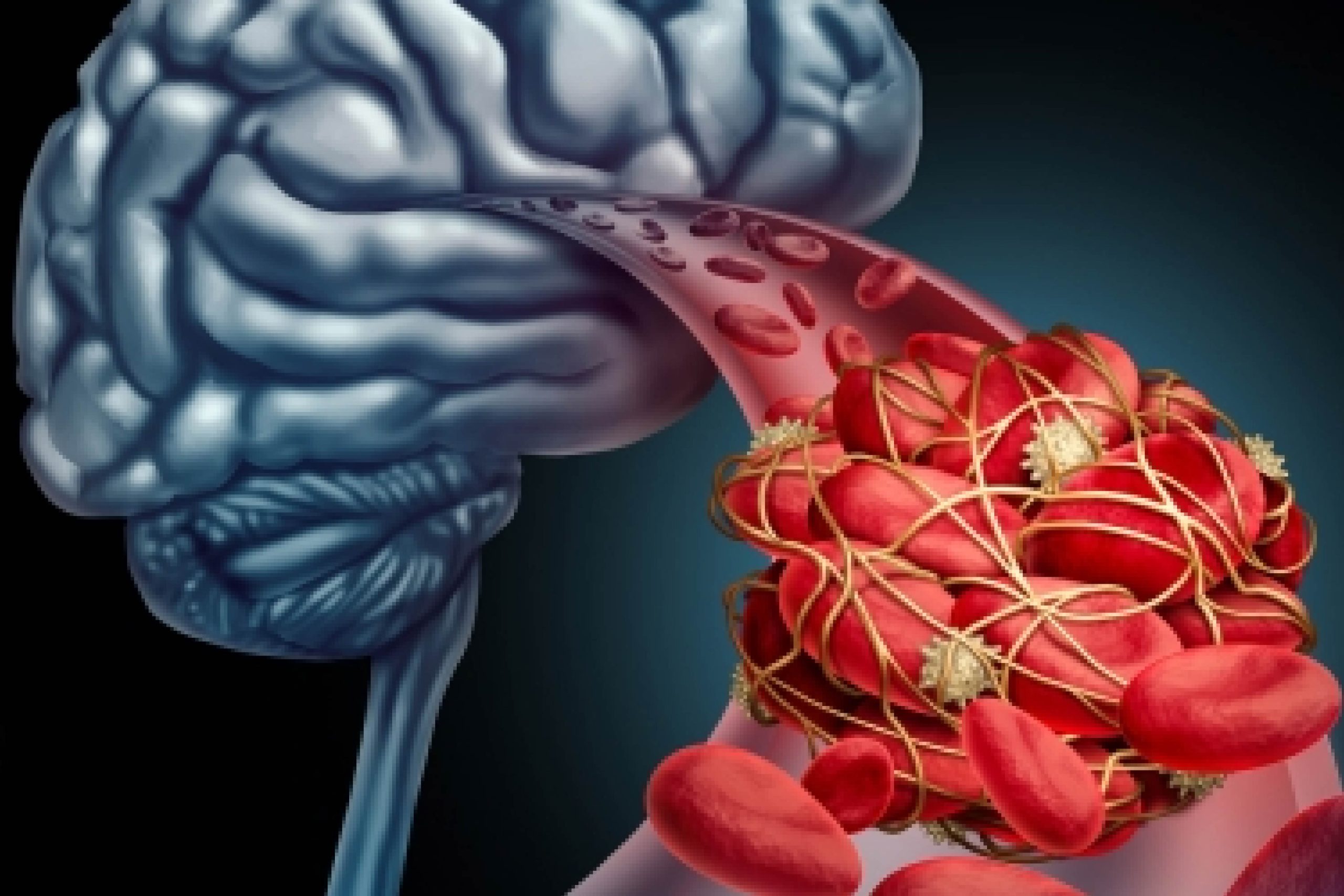
A mini-stroke, also known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA), is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain. It is similar to a stroke but the symptoms usually last for only a few minutes to a few hours and then disappear without leaving any permanent damage.
TIAs are caused by a blood clot or narrowing of a blood vessel in the brain. Risk factors for TIAs include high blood pressure, smoking, high cholesterol, diabetes, and a family history of stroke.
Symptoms
Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
Sudden trouble speaking or understanding speech
Sudden vision changes in one or both eyes
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination
Sudden severe headache with no known cause
Treatments
The treatment of a mini-stroke (TIA) aims to prevent a full-blown stroke from occurring in the future. Here are some common treatment options:
- Antiplatelet medications: These medications, such as aspirin or clopidogrel, help to prevent blood clots from forming and reduce the risk of another TIA or stroke.
- Anticoagulants: These medications, such as warfarin or dabigatran, also help to prevent blood clots. They may be prescribed if you have an irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation) or other conditions that increase the risk of blood clots.
- Blood pressure medications: High blood pressure is a major risk factor for TIAs and strokes. Medications to lower blood pressure, such as ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers, may be prescribed to help manage this condition.
- Cholesterol-lowering medications: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of TIAs and strokes. Statins and other medications can help to lower cholesterol levels.
- Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can also help to reduce the risk of future TIAs and strokes.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. They may recommend additional tests or procedures to evaluate your risk of future TIAs and strokes, and may adjust your medications or make other recommendations as needed.
A mini-stroke is a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain.
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body
- Sudden trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden vision changes in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination





