Appendicitis
Overview
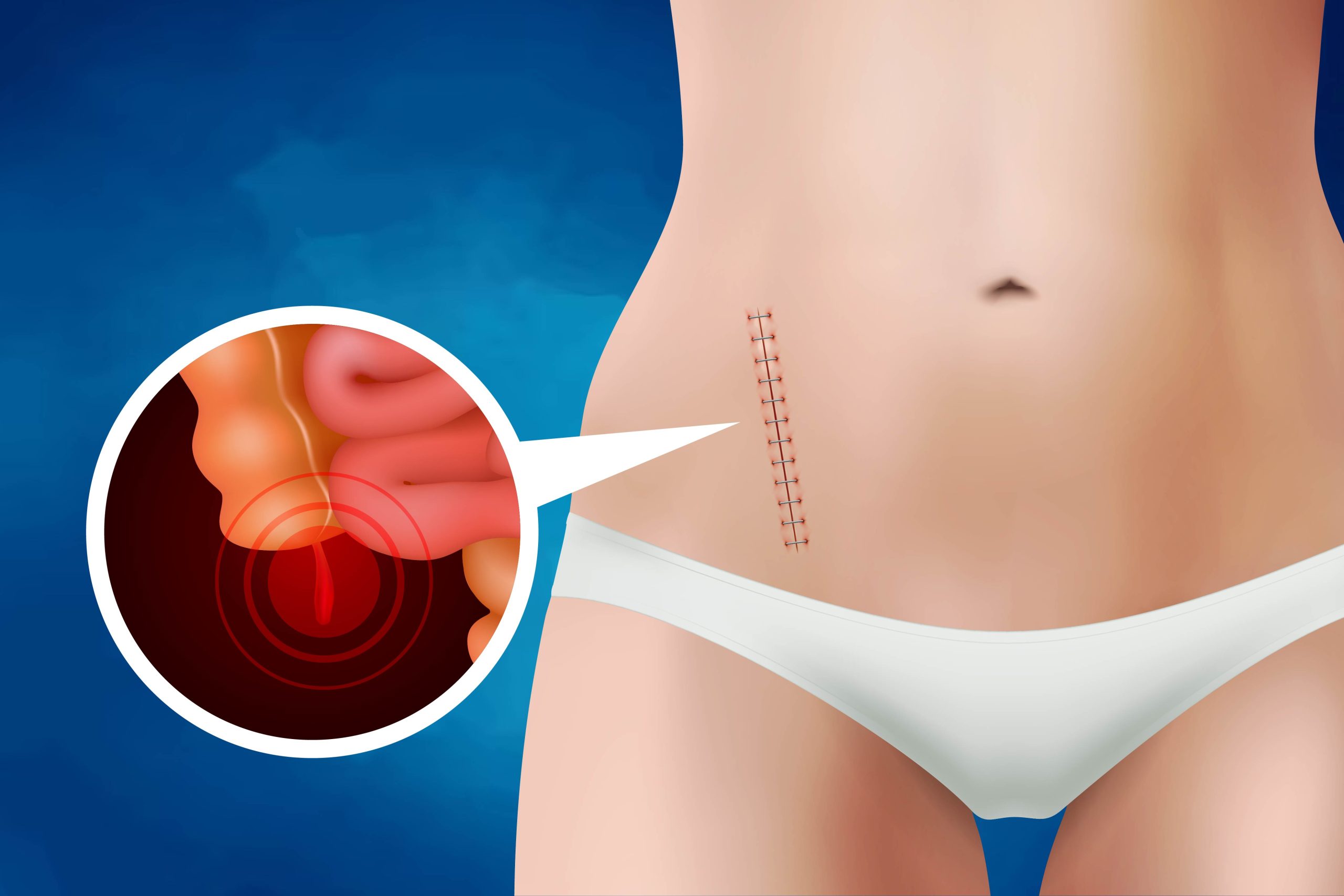
Appendicitis is a medical condition in which the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed and swollen. This can occur due to blockage of the appendix, typically by stool or a foreign object. The condition can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fever, and swelling and tenderness in the abdomen. If left untreated, appendicitis can lead to serious complications, such as the appendix bursting and causing infection throughout the abdominal cavity. Treatment for appendicitis typically involves surgical removal of the appendix, although antibiotics may be used in some cases. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery.
Symptoms
Some common symptoms of appendicitis include:
Abdominal pain
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Fever and chills
Abdominal swelling
Tenderness
Constipation or diarrhea
Difficulty passing gas or urine.
Treatments
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to avoid complications. The most common treatment for appendicitis is surgery to remove the appendix, a small organ located in the lower right side of the abdomen.
The surgical procedure to remove the appendix is called an appendectomy, and it can be performed either through open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. In open surgery, a single large incision is made in the abdomen to remove the appendix, while in laparoscopic surgery, several small incisions are made, and a small camera is inserted to guide the surgeon in removing the appendix.
In some cases, antibiotics may be used as an alternative to surgery for the treatment of appendicitis. This is typically reserved for cases where the inflammation is mild and there is no rupture of the appendix. However, it is important to note that antibiotics alone may not be effective in all cases of appendicitis and surgery may still be required.
If the appendix has ruptured, it may be necessary to drain any abscesses that have formed before the appendectomy can be performed. In some cases, a course of antibiotics may be necessary after surgery to prevent infection.
It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect that you may have appendicitis, as delaying treatment can increase the risk of complications and make treatment more difficult.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine, typically requiring surgical removal.
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Abdominal swelling
- Tenderness
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Difficulty passing gas or urine





